
👩🏻💻 What are Email Compromise Scams
Email compromise scams, or Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams, are a type of cybercrime in which fraudsters use email to trick individuals or organizations into transferring money or sensitive information.
In these scams, the fraudster will typically impersonate a trusted individual or entity, such as a CEO, vendor, or supplier, and request that the victim transfer money or share confidential information. The email appears legitimate, with persuasive language and logos, and may come from a legitimate email address or domain.
BEC scams are often successful because they prey on human nature. The attacker often uses social engineering techniques to create a sense of urgency or fear to persuade the victim to act quickly without thinking critically about the request.
These types of scams can have devastating consequences for individuals and organizations, resulting in significant financial losses or the exposure of sensitive information.
☝🏼 Potential Costs of Email Compromise Scams
BEC scams can be very costly for businesses. In 2022, the IC3 received 21,832 Business Email Compromise (BEC)/ Email Account Compromise (EAC) complaints with nearly $2.7 billion in adjusted losses. If you receive an email that seems suspicious, it’s essential to take a step back and think critically about the request before taking action.

📌 To protect your business from BEC scams, you can follow a list of best practices, which includes:
Utilize strong passwords
Passwords are often the first line of defense against cyber attacks. Make sure to use strong passwords that are difficult to guess or crack. Consider using a password manager to generate and store unique passwords for each account.
Implement multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring a second form of authentication, such as a code sent to your phone or a fingerprint scan. This can help prevent unauthorized access to your accounts, even if your password is compromised.
Monitor email accounts
Keep a close eye on your email accounts for any suspicious activity, such as unauthorized logins or unusual email activity. You can also set up alerts for any changes to your account settings or forwarding rules.
Be wary of suspicious emails
Train your employees to recognize and report suspicious emails, such as those that ask for sensitive information or contain suspicious links or attachments. Encourage them to verify the sender’s identity and double-check any requests before taking any action.
🔐 Protecting Sensitive Information
Sensitive information such as financial data, customer information, trade secrets, and intellectual property are valuable assets to your business. Protecting this information from unauthorized access and theft is crucial to maintain your business’s reputation and success.
Here are some best practices to protect sensitive information in your business organization:
Utilize Encryption
Encryption is converting data into a form that unauthorized individuals cannot read. This is done using an encryption algorithm, a mathematical formula that scrambles the data so that only someone with the correct key can unscramble it. Encrypting your sensitive data ensures that if it is intercepted or stolen, it is unreadable and unusable to anyone who doesn’t have the decryption key.
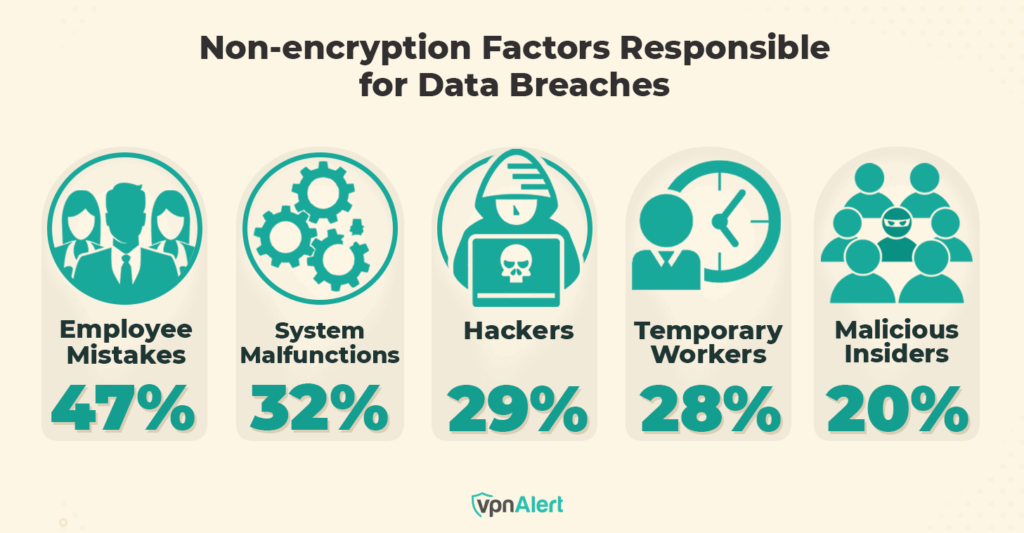
Employee mistakes are still a significant threat to sensitive data, irrespective of encryption. As of 2022, employee mistakes accounted for 47% of all sensitive data breaches in most organizations. Other contributing factors included system malfunctions (32%), hackers (29%), temporary workers (28%), and malicious insiders (20%).
The encryption process typically works in the following steps:
- The data is divided into blocks of a certain size.
- A random key is generated.
- The key is used to encrypt the data blocks.
- The encrypted data is transmitted to the recipient.
- The recipient uses the key to decrypt the data.
The encryption process can be used to protect a variety of data, including:
- Data in transit: This is data that is being transmitted over a network, such as the Internet.
- Data at rest: This is data that is stored on a physical device, such as a hard drive or a USB drive.
- Data in use: This is data that is being processed by a computer system.
Encryption is a critical security technology that helps to protect data from unauthorized access, disclosure, modification, or destruction. Businesses, governments, and individuals use it to safeguard various sensitive data.
Educate Employees
Employees are the first line of defense against cyber attacks. Educate them on the importance of protecting sensitive information. Train them on the best practices, such as creating strong passwords, being cautious of phishing emails, (according to the IC3 Report 2022, Phishing is on the top five crime types since 2018), and never sharing sensitive information over unsecured channels. Conduct regular security awareness training to inform employees about the latest security threats and how to prevent them.
Establish Security Protocols
Assess your organization’s security needs. For example, what data do you need to protect? What are the potential threats to that data? Once you understand your organization’s security needs, you can start developing a security protocol that addresses those needs.
Establish clear security protocols and procedures for handling sensitive information. Implement access controls such as role-based access control (RBAC), two-factor authentication (2FA), and firewalls to restrict sensitive data access to those who need it. Create a data classification policy that outlines how to handle sensitive data, including who has access to it, how it should be stored, and when it should be destroyed.
Lastly, consider using a data removal service to remove your employees’ PII from data broker sites. Reduce your company’s risks for phishing, social engineering, hacking, identity theft, fraud, harassment, and physical violence. Try Optery’s Business Plan!
